LABORATORIES
Neuroimaging group
Neuroimaging group
Research
Team
Publications
Contact
Others
Research
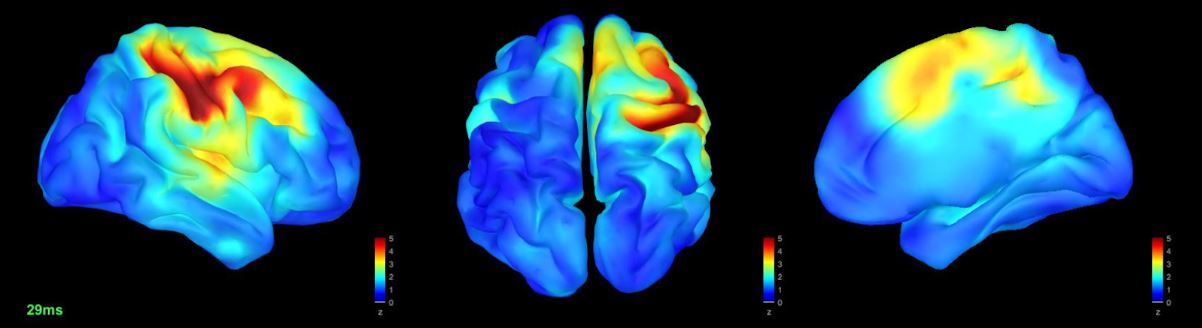
Lines of investigation
1) Healthy brain
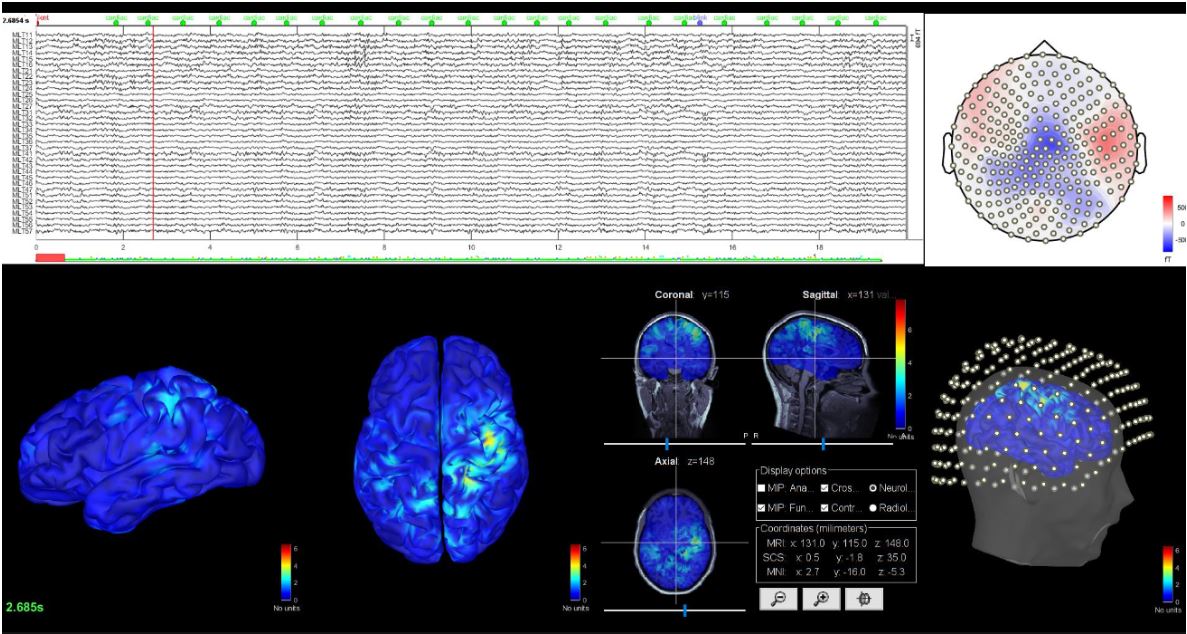
One of our main objectives is to characterize brain activity in healthy people, studying oscillations, synchronization between regions and connectivity, to better understand how the brain works and how it communicates. Through specific studies we also try to identify the underlying oscillatory mechanisms that arise in different cognitive processes. We study brain structure and activity using complementary neuroimaging techniques, following a multimodal and multidisciplinary approach that allows us to integrate together the different results obtained.
2) Clinical applications
The ultimate goal of our group is to improve people’s lives, so we study how the activity characterized in a healthy population is altered in different neurological conditions, such as aging, Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, chronic pain or blindness. We also evaluate specific neurorehabilitation programs that use motor, cognitive, or neurofeedback interventions. We aim to find common elements to better understand the global functioning of the brain.
3) Open and reproducible neuroimaging
We lead different initiatives to help neuroimaging research be more open and reproducible.
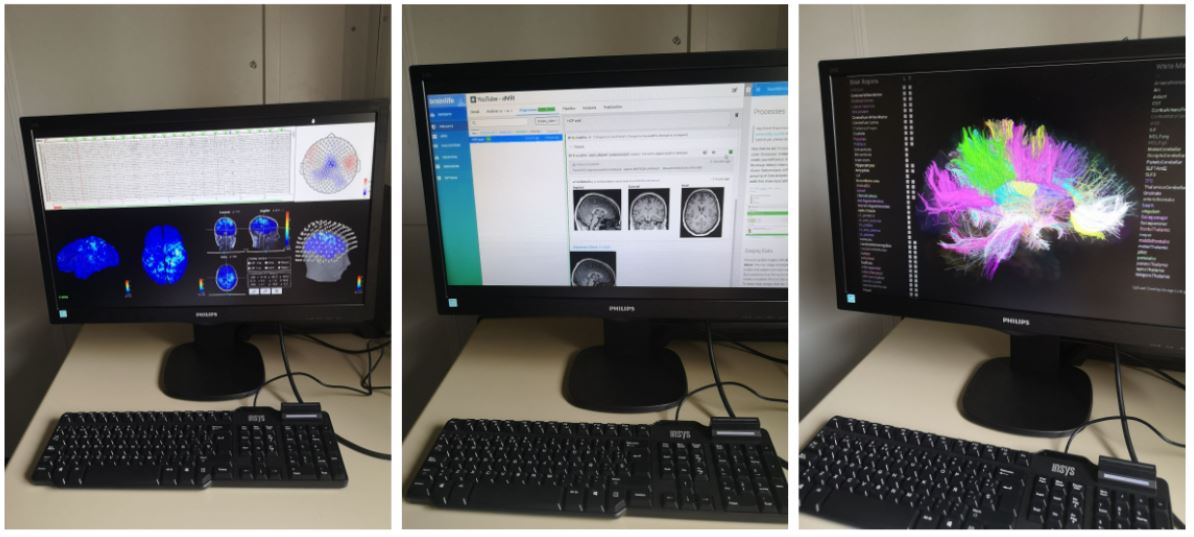
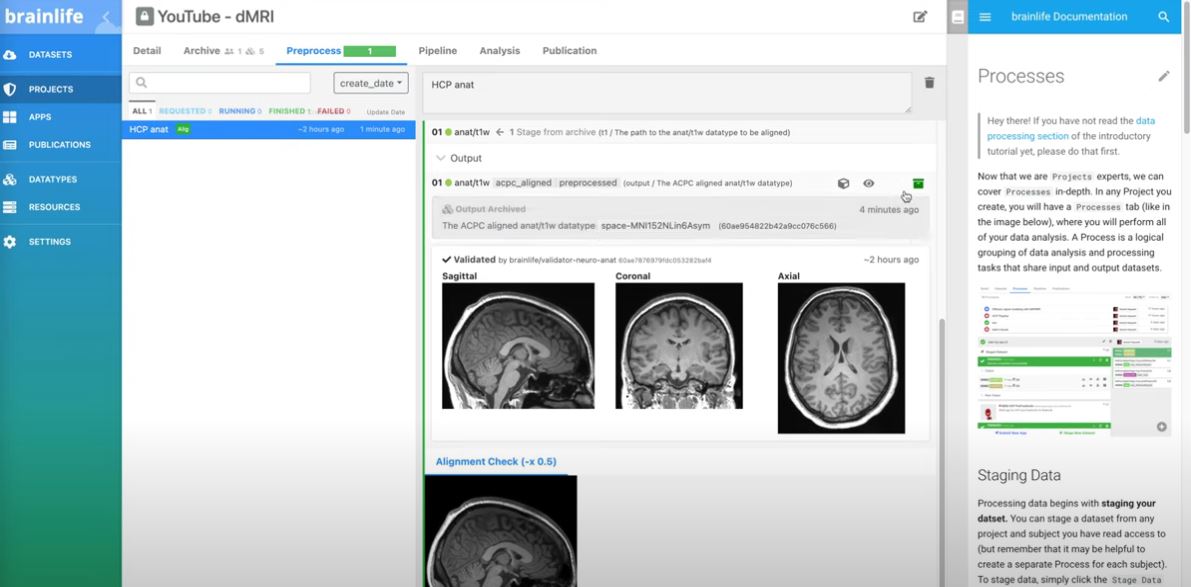
– Open software: We contribute to the development of tools such as Brainlife, a cloud platform for the safe and reproducible analysis of neuroscience data, Brainstorm and MNE-Python, collaborative applications for the analysis of brain recordings obtained from different modalities, such as MEG, EEG , ECoG, iEEG and fNIRS, or HERMES, a tool for the analysis of functional brain connectivity.
– Open repositories: We created the first repository primarily dedicated to magnetoencephalography data, The Open MEG Archive (OMEGA), in collaboration with the Montreal Neurological Institute of McGill University. We also contribute various datasets to OpenNeuro.
– Open standards: We lead the international consortium for the development of the Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS), the first common standard for organizing, describing and sharing neuroimaging data. We work developing extensions to accommodate new neuroimaging modalities and their derivatives resulting after their preprocessing and analysis.
In addition, we also participate in several projects that aim to replicate different scientific results: such as EEGManyLabs, EEGManyPipelines, Think/NoThink paradigm, Multi100 project. We actively collaborate internationally to make neuroimaging more open and reproducible and provide resources to this end.
Team

Principal Investigator
Guiomar Niso
Principal Investigator
Google Scholar
ORCID: 0000-0001-5872-8924
Personal website: https://guiomarniso.com
Group

Fiona Ye Rojo Acero
BSc in Biomedical Engineering
Universidad Carlos III de Madrid

Álvaro Mozas Robles
MSc in Advanced therapies in biomedicine
Universidad Francisco de Vitoria
Publications
List of most relevant publications
See more here.
- Niso G., Romero E., Moreau, J.T., Araujo A. & Krol, L. (2023). Wireless EEG: A Survey of Systems and Studies. NeuroImage, 119774. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119774
- Luke R., Oostenveld R., Cockx H., Niso G., Shader M.J., …, Pollonini L. (2023) fNIRS-BIDS, the Brain Imaging Data Structure Extended to Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. OSF Preprint: https://osf.io/7nmcp
- Niso G., Botvinik-Nezer, R., Appelhoff, S., De La Vega, A., Esteban, O., Etzel, J. A., … & Rieger, J. (2022). Open and reproducible neuroimaging: from study inception to publication. NeuroImage, 119623. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119623
- Govaart, G., Schettino, A., Helbling, S., … Niso, G., … & Paul, M. (2022). EEG ERP preregistration template. MetaArXiv. doi: https://doi.org/10.31222/osf.io/4nvpt
- Bourget, M. H., Kamentsky, L., Ghosh, S. S., … Niso, G.,… & Cohen-Adad, J. (2022). Microscopy-BIDS: an extension to the Brain Imaging Data Structure for Microscopy Data. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 377. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.871228
- Niso G., Krol, L., Combrisson, E., Dubarry, A. S., Elliott, M., François, C., … & Chaumon, M. (2021). Good Scientific Practice in EEG and MEG Research: Progress and Perspectives. Neuroimage, 119056. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119056
- Norgaard, M., Matheson, G. J., Hansen, H.D., … Niso, G.,… & Ganz, M. (2022). PET-BIDS, an extension to the brain imaging data structure for positron emission tomography. Scientific data, 9(1), 1-7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01164-1
- Niso G., Tjepkema-Cloostermans, M. C., Lenders, M. W., & de Vos, C. C. (2021). Modulation of the Somatosensory Evoked Potential by Attention and Spinal Cord Stimulation. Frontiers in neurology, 1311. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.694310
- Levitis, E., Van Praag, C. D. G., Gau, R., Heunis, S., … Niso, G.,… & Maumet, C. (2021). Centering inclusivity in the design of online conferences—An OHBM–Open Science perspective. GigaScience, 10(8), giab051. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giab051
- Pavlov, Y., Adamian, N., Appelhoff, S., Arvaneh, M., Benwell, C., Bland, A., Bradford, D., Bublatzky, F., Busch, N., … Niso, G.,…, Mushtaq, F. (2021). # EEGManyLabs: Investigating the replicability of influential EEG experiments. Cortex. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2021.03.013
- Müller F. / Niso G., Samiee S., Ptito M., Baillet S., Kupers R. (2019) A thalamocortical pathway for fast rerouting of tactile information to occipital cortex in congenital blindness. Nature Communications 10(1), 5154. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13173-7
- Xifra-Porxas A., Niso G., Larivière S., Kassinopoulos M., Baillet S., Mitsis G.D., Boudrias M.H. (2019) Older adults exhibit a more pronounced modulation of beta oscillations when performing sustained and dynamic handgrips. Neuroimage 201, 116037. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116037
- Chholak, P., Niso, G., Maksimenko, V.A., Kurkin, S.A., Frolov, N.S., Pitsik, E.N., Hramov, A.E. and Pisarchik, A.N. (2019) Visual and kinesthetic modes affect motor imagery classification in untrained subjects. Scientific reports 9(1), 9838. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46310-9
- Larivière S., Xifra-Porxas A., Kassinopoulos M., Niso G., Baillet S., Mitsis G.D., Boudrias M.H. (2019) Functional and effective reorganization of the aging brain during unimanual and bimanual hand movements. Human brain mapping, 40(10), 3027-3040. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.24578
- Niso G., Tadel F., Bock E., Cousineau, M., Santos, A., Baillet S. (2019) Brainstorm pipeline analysis of resting-state data from the Open MEG Archive. Frontiers in neuroscience 13, 284. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00284
- Tadel F., Bock E., Niso G., Mosher J.C., Cousineau, M., Pantazis D., Leahy R.M., Baillet S. (2019) MEG/EEG group analysis: the Brainstorm workflow. Frontiers in neuroscience 13, 76. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00076
- Niso G., Gorgolewski K.J., Bock E., Brooks T.L., Flandin G., Gramfort A., Henson R.N., Jas M., Litvak V., Moreau J., Oostenveld R., Schoffelen J.M., Tadel F., Wexler J., Baillet S. (2018) MEG-BIDS: an extension to the Brain Imaging Data Structure for magnetoencephalography. Scientific Data 5, 180110. https://www.nature.com/articles/sdata2018110
- Soriano M.C., Niso G., Clements J., Ortín S., Carrasco S., Gudín M., Mirasso C.R., Pereda E.(2017) Automated detection of epileptic biomarkers in resting-state interictal MEG data. Frontiers in neuroinformatics 11, 43. doi: http://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2017.00043
- Niso G., Rogers C., Moreau J.T., Chen L.Y., Madjar C., Das S., Bock E., Tadel F., Evans A.C., Jolicoeur P., Baillet S. (2016). OMEGA: The Open MEG Archive. NeuroImage 124, 1182-1187. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.04.028
- Das S., Glatard T., MacIntyre L.C. , Madjar C., Rogers C., Rousseau M.E., Rioux P., MacFarlane D., Mohaddes Z., Makowski C., Niso G., Moreau J.T., Evans A.C. (2016). The MNI data-sharing and processing ecosystem. NeuroImage 124, 1188-1195. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.08.076
- Carrasco S., Niso G., Canuet L., Burriel L., Maestú F., Gudín M. (2016). Praxis induced seizures in a juvenile myoclonic epilepsy patient: MEG and EEG coregistration study. Epilepsy & Behavior Case Reports 5, 1-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebcr.2015.10.002
- Niso G., Carrasco S., Gudín M., Maestú F., del-Pozo F., Pereda E. (2015). What graph theory really tells us about resting state interictal MEG epileptic activity. NeuroImage Clinical 8, 503-515, ISSN 2213-1582, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2015.05.008
- Ariza P., Solesio-Jofre E., Martinez-Huartos J., Pineda-Pardo, J.A., Niso G., Maestú F., Buldú J.M. (2015). Evaluating the effect of ageing on interference resolution with time-varying complex networks analysis. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 255. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00255
- Lopez M.E., Aurtenetxe S., Pereda E., Cuesta P., Castellanos N.P., Bruña R., Niso G., Maestú F., Bajo R. (2014). Cognitive reserve is associated with the functional organization of brain in healthy aging: A MEG Study. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 6, 125. ISSN: 1663-4365. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00125
- Niso G., Bruña R., Pereda E., Gutiérrez R., Bajo R., Maestú F., del-Pozo F. (2013). HERMES: towards an integrated toolbox to characterize functional and effective brain connectivity. NeuroInformatics 11 (4), 405-434. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-013-9186-1
Contact
Where to find us
MA-03
Instituto Cajal CSIC. Avda. Doctor Arce, 37. 28002. Madrid
Write us
Email address:
Others
Awards and recognitions
2023 Guiomar Niso. Medal for Young Researchers by the Royal Academy of Engineering of Spain (link)
2023 Guiomar Niso. International Open Science Prize by The Neuro – Irv and Helga Cooper Foundation to the Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS) (link)
2023 Guiomar Niso. The British Neuroscience Association (BNA) Credibility in Neuroscience Price to Team Credibility with #EEGManyLabs Project (link).
2022 Guiomar Niso. Ada Byron Award to Women Technologist 2022, University of Deusto (link)
2022 Guiomar Niso. Member of the Young Academy of Spain (link)

Neuroscience Research Center dependent on the CSIC. Founded in 1920 and initially directed by Santiago Ramón y Cajal. World reference in the study of the brain. Custodian of the Cajal Legacy.
Activities

